Rylah's Study & Daily Life
Effective C++ : Chapter 01. Accustoming Yourself to C++ 본문

번역서를 보는 것이 아니라 원서를 보기 시작
일주일 안에 끝났으면 좋겠다.
Chapter 1: C++에 익숙해지자.
Item 1: View C++ as a federation of languages.
- C++를 언어의 연합체로 바라보자
C++에서 고려해야할 하위 요소 4가지
1. C. 하위레벨 언어
2. 객체 지향 C++
3. Template C++
4. STL
이러한 하위 언어 요소들이 모여있는 연합체라고 생각하는 것이 맞다.
Item 2: Prefer consts, enums, and inlines to #defines.
- #define을 쓰기 전에 const, enum, inline을 사용할 수 있는 지 고려하자.
#define에 선언된 항목은 컴파일러에서 찾아볼 수 없다.
전처리기에서 이미 제거되기 때문이다.
오류가 발생했을 때 혼동하기 쉽다.
const와 같이 선언하면 컴파일러에서도 확인할 수 있다.
상수의 경우에는 enum을 사용하는 것 또 한 방법이다.
- 정적 멤버로 만들어지는 정수류 타입의 클래스 내부 상수는 '정의'가 없어도 된다.
✦ 단순 상수의 경우 #defines보다 const 객체 또는 열거형을 선호합니다.
✦ for 함수와 유사한 매크로의 경우 #defines보다 인라인 함수를 선호합니다.
Item 3: Use const whenever possible.
- 가능한 곳에서는 const를 붙이자.

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
// 컴파일러는 비트수준 상수성만 보장해준다.
// 우리는 논리적 상수성을 고려해서 프로그래밍해야한다.
class Book {
private:
int* data;
int num;
mutable int callCnt;
public:
int* getData() const {
// It is valid in bitwise constness, but invalid in logical constness.
return data; // compile ok.
}
int& getData(int idx) const {
// It is valid in bitwise constness, but invalid in logical constness.
return data[idx]; // compile ok.
}
int& getNum() const {
// It is both invalid in bitwise constness and logical constness.
return num; // compile error.
}
void call() const {
// It is invalid in bitwise constness, but valid in logical constness.
++callCnt; // compile ok.
}
};
// enum, typedef, class의 유효범위는 선언된 scope내부, 그리고 어디서나 선언될 수 있다.
// 단, template, namespace는 global혹은 namespace 안에서만 선언될 수 있다.
namespace Test {
class A {
int v;
};
};
template<typename T>
class AA {
T aa;
};
int main()
{
template<typename T> // ERROR
class AAA {
T aa;
};
namespace NNNN { // ERROR
class A {
};
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
enum { POS = 3 }; // NO ERROR
typedef int INT;
INT a[POS];
class BBB {
};
BBB q;
template<typename T> // ERROR
class AAAA {
T aa;
};
AA<int> k;
AAA<int> kk;
AAAA<int> kkk;
namespace TTT { // ERROR
class A {
};
};
}
BBB rr;
INT b[POS];
}
|
cs |
✦ const를 붙여 선언하면 컴파일러가 사용상의 에러를 잡아내는 데 도움을 준다.
✦ 컴파일러 쪽에서는 비트수준 상수성을 지켜야 하지만, 우리는 논리적 상수성을 사용해서 프로그래밍해야한다. (mutable keyword)
✦ 상수 멤버와 비상수 멤버 함수이 똑같을 경우엔 비상수버전이 상수버전을 호출함으로서 코드 중복을 피할 수 있다.
Item 4: Make sure that objects are initialized before they’re used.
- 객체를 사용하기 전에 초기화를 꼭 하자.
멤버 이니셜라이저로 초기화 한 것은 변수를 복사하지 않지만 그냥 생성자로 멤버 변수를 초기화 하려고하면 객체가 하나 생성되고 Move 연산이 일어난 뒤에 사라진다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
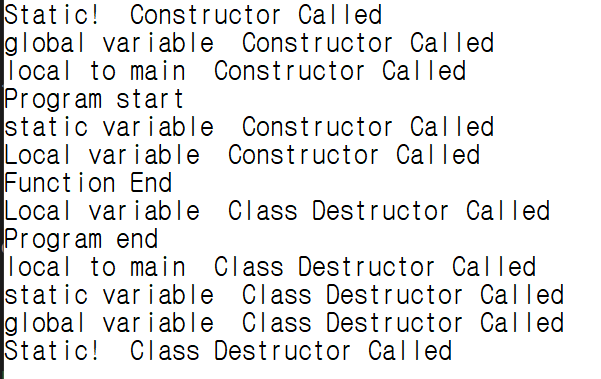
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyClass
{
public:
MyClass(const char* name) : _name(name)
{
cout << _name << " Constructor Called" << endl;
}
~MyClass()
{
cout << _name << " Class Destructor Called" << endl;
}
string _name;
static MyClass _staticMember; // static member
};
MyClass MyClass::_staticMember("Static!");
MyClass _staticMember("global variable");
void foo()
{
static MyClass _staticMember("static variable");
static int num = 10; // POD type, init before enter main function
MyClass class2("Local variable");
cout << "Function End" << endl;
}
int main()
{
MyClass mc("local to main");
cout << "Program start" << endl;
foo();
cout << "Program end" << endl;
return 0;
}
|
cs |
이 뿐만 아니라 디폴트 생성자를 이용해서 삽입했을 경우와 멤버 이니셜라이저로 초기화 했을때를 비교해보자
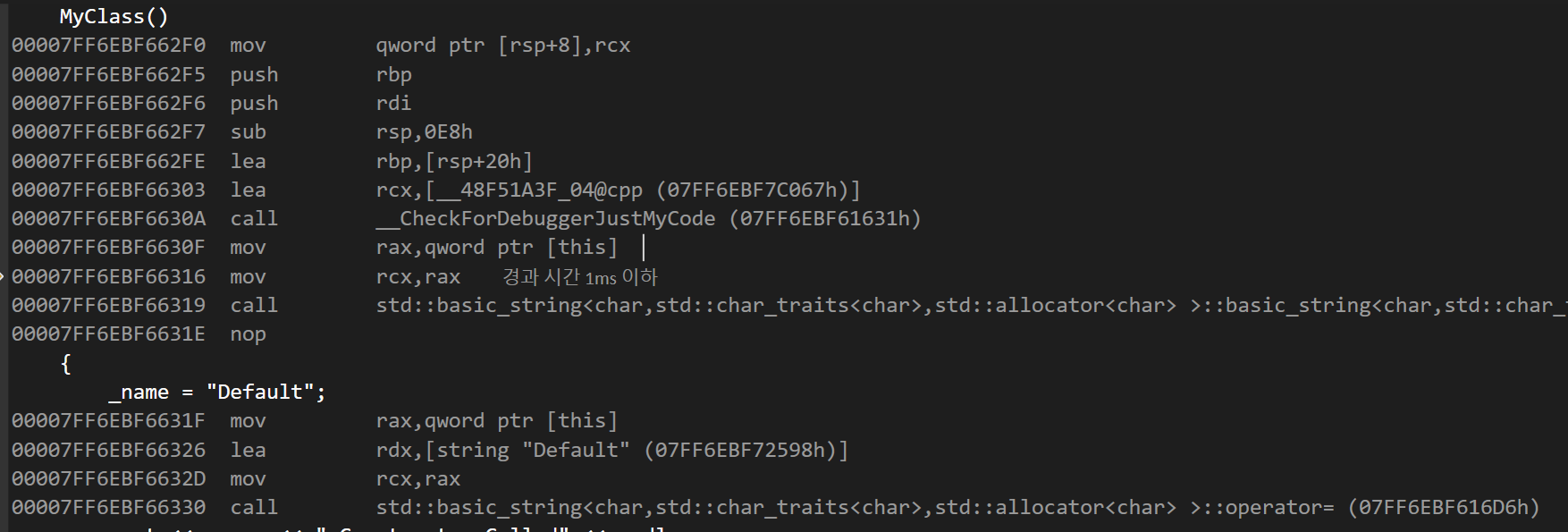
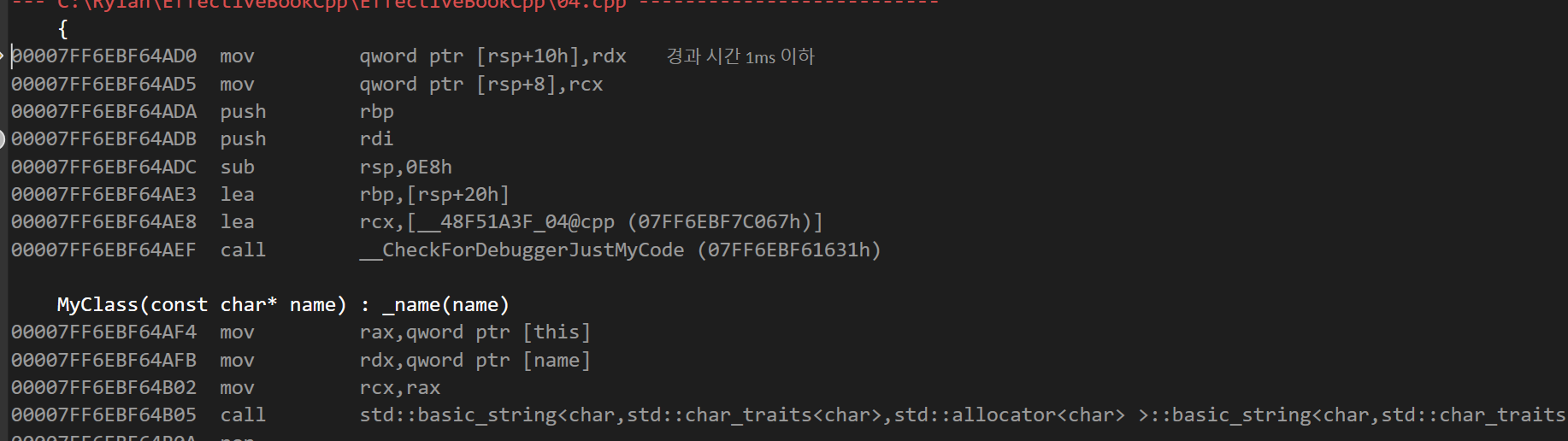
연산이 확 줄었다는 것을 알 수 있다.
이 때문에 세간에서 멤버 이니셜라이저로 초기화 하는 것이 Move 연산이 줄어들면서 성능상의 이득이 있다고 하는 것이다.
'Study > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Modern C++ : 03. C++ Build : Dynamic Library (Shared Library) (0) | 2022.03.29 |
|---|---|
| Modern C++ : 03. C++ Build : Static Library (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| 01. Thread (0) | 2022.03.28 |
| rax eax (0) | 2022.03.24 |
| .bss .data .rodata (0) | 2022.03.23 |


